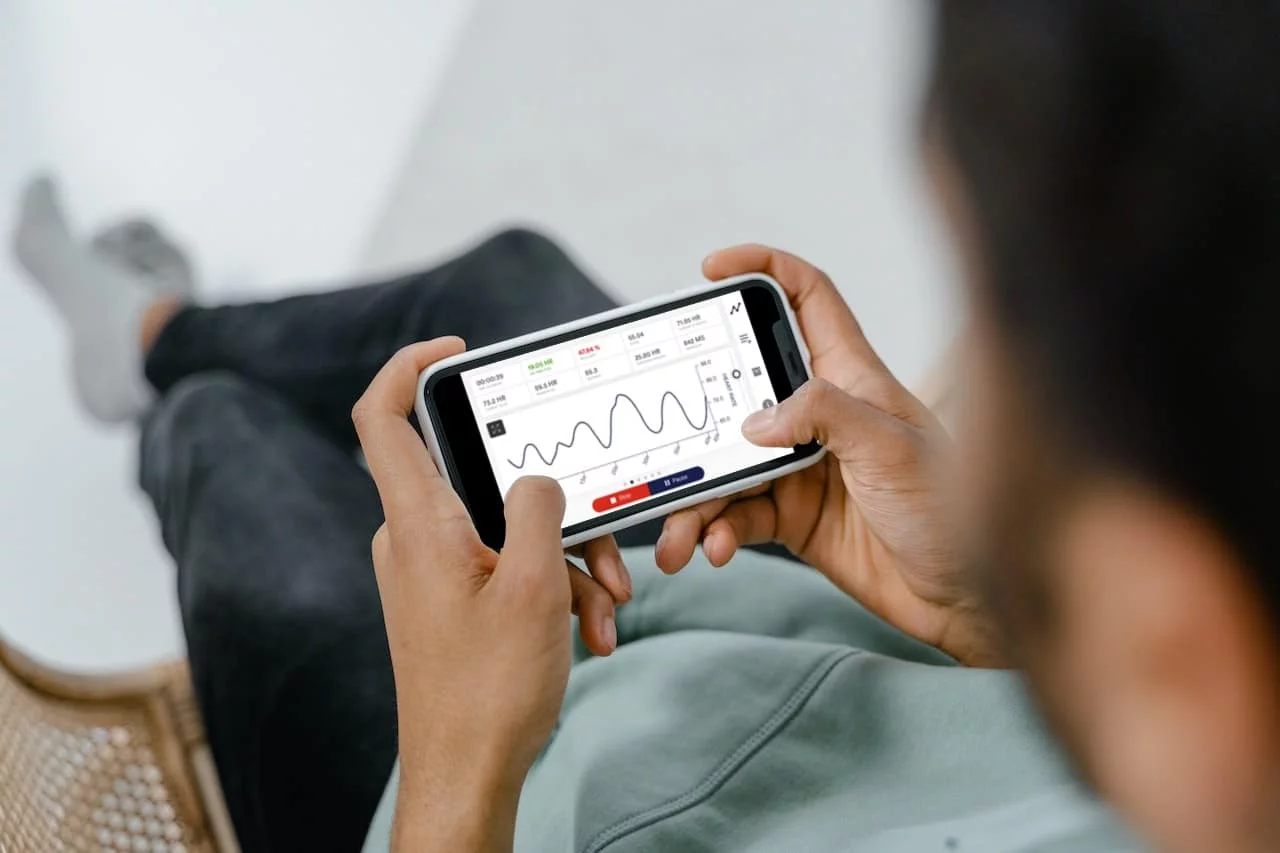
Biofeedback training is a scientifically-based method that makes your body’s stress responses visible and helps you train targeted relaxation. With mobile sensors like the eSense devices, you can practice effective stress training conveniently at home. This practical guide shows you step by step how to get started.

Niko Rockensüß
Born in Berlin in 1983, Niko Rockensüß is a leading expert in the field of biofeedback and neurofeedback with over 20 years of professional experience. As Managing Director of Mindfield Biosystems Ltd., he has made a significant contribution to the development and dissemination of innovative biofeedback and neurofeedback solutions.
The integration of biofeedback into everyday life at home offers an excellent opportunity to continuously work on reducing stress. With the help of various biofeedback devices such as heart rate monitors, respiratory monitors, skin temperature meters, EMG devices and skin conductance meters, you can analyze your stress levels. These innovative instruments enable the detection of various physical signals, including increased skin conductance or increased heart rate, and thus effectively support the stress management process.
These devices make it possible to recognize stress signals at an early stage and take targeted action to counteract them. You can learn to apply various relaxation techniques or identify and avoid stress triggers.
This blog article provides an overview of how these home devices can be used effectively for biofeedback against stress and how operant conditioning can have an effect. It explains how repeated use of relaxation techniques or targeted breathing exercises can provide positive reinforcement and thus reduce stress levels in the long term. Biofeedback devices therefore offer a practical way to reduce stress from home and at the same time get to know your own physical reactions better.
Biofeedback self-application at home
Biofeedback devices are instruments that are used to measure and monitor the body’s response to stress. The preparation and equipment for self-application of biofeedback at home is relatively simple, provided you have the right device. There are a variety of biofeedback devices on the market, from simple heart rate monitors to more complex devices that can measure various physiological parameters such as skin conductance, respiratory rate or muscle tension. Modern devices are often connected to apps that analyze and record the recorded data. By measuring these physiological parameters, people can learn to recognize and control their physical reactions to stress.
Self-application of biofeedback at home can help to reduce stress and promote general relaxation. By learning how your body reacts to stress, you can develop effective relaxation techniques and better control your stress responses. This can help to reduce the negative effects of stress on physical and mental health. Regular use of biofeedback training at home can therefore be an effective method of stress management and self-regulation.
Preparation of the equipment (biofeedback devices)
The following paragraphs describe how to use biofeedback devices correctly at home. This is explained in 8 steps to ensure that the application is effective and safe. This preparation is suitable for various types of devices, including heart rate monitors, skin conductance meters (stress meters), skin temperature meters, respiratory sensors and muscle tone meters.
It is important to prepare the equipment properly to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Proper preparation of the equipment includes placing and positioning the sensors and checking the batteries or power supply. In addition, the user manuals should be read carefully and the manufacturer’s instructions followed in order to use the equipment properly.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the biofeedback equipment is used correctly to provide accurate and meaningful data. This is crucial in order to reap the full benefits of biofeedback at home and effectively combat your stress levels.
Step 1: Create a relaxed environment for biofeedback training
For biofeedback training against stress, it is important to create a relaxed environment, as stress can have a direct impact on physiological readings. When a person is in a stressful environment, this can lead to increased blood pressure, faster heartbeat, increased skin conductance, cold hands and muscle tension. This can impair the effect of the biofeedback measurements, as the physiological values are already altered by the stressful environment.
A relaxed environment is therefore essential to achieve accurate and effective biofeedback training results. A calm and pleasant environment can reduce stress levels, normalize the heartbeat, calm breathing, lower skin conductance and reduce muscle tension, which gives the measurements the necessary basis.
In addition, the environment also plays an important role in creating a pleasant and positive experience for the participants. A relaxed environment can help participants feel comfortable and safe, which improves the effectiveness of the training.
Step 2: Attaching the sensors and electrodes for biofeedback training
The correct placement of the sensors is crucial in order to obtain precise and reliable data during biofeedback training. Especially with skin conductance meters and heart rate monitors, respiration meters, skin temperature meters and EMG devices, careful placement of the sensors is essential. Here are some aspects to look out for:
Skin conductance meter:
- Preparation of the skin: Make sure that the skin to which the electrodes are to be attached is clean, dry and free of lotions or creams. Optimum skin preparation ensures good electrical conductivity.
- Attaching the electrodes: Place the electrodes according to the device instructions. Electrodes are usually attached to fingertips or palms. Make sure that the electrodes are tight, but not too tight, to avoid skin irritation.
- Contact check: Before starting training, carry out a contact check to ensure that the electrodes adhere properly to the skin and make stable contact.
Heart rate monitor:
- Correct placement of the chest strap: Wear the chest strap according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Place it directly under the chest and over the sternum. The strap should be tight but not too tight to ensure correct measurements.
- Electrode humidity: Some heart rate monitors use electrodes that need to be moistened with contact spray. Make sure that the electrodes are sufficiently moistened to ensure good electrical conductivity.
- Checking the signal quality: Before you start training, check the signal quality. Make sure that the heart rate monitor is receiving a stable signal and that there is no interference.
Breathalyzers:
- Correct placement of the breathing harness: Place the belt either around the chest or around the abdomen, depending on your preferred measurement of chest or abdominal breathing. For effective measurement and training of deep abdominal breathing, placement around the abdomen is usually recommended. The belt should fit loosely and not be restrictive. Minimal pressure on the spring of the sensor unit is sufficient.
-
- Attaching the sensor unit: After you have put on the belt, slide the sensor unit under the belt. Connect the cables from the breath monitor to the sensor’s push-button connectors If your device no longer has a microphone input, an adapter may be required, especially for newer Apple iPhones/iPads. Such an adapter is available from the manufacturer and ensures a smooth function.
- Ensure freedom of movement: Make sure that the belt is loose enough not to restrict your movements. A light pressure on the sensor unit is sufficient to enable a precise measurement. Note that the belt should not create any uncomfortable tension to ensure a comfortable biofeedback experience .
Skin temperature sensor:
- Hold on tight: Simply hold the sensor between your index finger and thumb to ensure stable positioning.
- Leukosilk (medical plaster): Alternatively, you can attach the sensor to your finger or the palm of your hand using adhesive tape. You can obtain roll adhesive tape from any pharmacy. This method allows the sensor to be attached to a finger or the palm of the hand and also offers comfort during longer measurements.
- Finger Clip: Our recommended method of attachment is the finger clip. This does not stick as no adhesive is used, and its open design ensures that no heat build-up occurs. The finger clip is particularly suitable for longer measurements and allows the temperature sensor to be optimally fixed in place.
- Velcro tape: A Velcro strap is available for convenient attachment, allowing you to attach the sensor securely to your finger. This method requires no additional equipment and is particularly convenient for longer measurements. The Velcro strap is included with every skin temperature sensor.
Electromyography:
- Prepare the electrode cable set: Remove the electrode cable set from the packaging. Five electrode cables are included: black, white, yellow, red and green. Note that the yellow electrode cable is the earth electrode.
-
- Prepare 1-channel measurement: For a 1-channel measurement, use the electrodes black (channel 1+), white (channel 1-) and yellow (ground).
- Prepare 2-channel measurement: For a 2-channel measurement, use the electrodes black (channel 1+), white (channel 1-), yellow (ground), red (channel 2+) and green (channel 2-).
- Skin preparation: Clean the areas of skin to which you want to attach the electrodes with the enclosed alcohol swabs or isopropyl alcohol.
- Attach electrodes: Remove the appropriate number of EMG surface electrodes from the packaging, attach the electrodes to the cable ends before placing them on the clean skin. Remove the protective film from the electrodes and stick them to the skin. If you have not already done so, plug the electrode cables into the matching color sockets on the EMG device.
- Seal the packaging: Do not forget to seal the packaging of the EMG surface electrodes airtight to prevent them from drying out and to ensure correct readings.
Correct placement of the sensors ensures accurate recording of physiological parameters, which in turn leads to effective biofeedback training. Precise placement prevents falsification of the data and provides you with reliable feedback on your physiological states during training.
Step 3: Measurement and perception of biofeedback values
During the measurement, you receive immediate feedback on your physiological states. This feedback can be provided visually, acoustically or via other sensory perceptions. For example, an increase in heart rate can be indicated by an acoustic signal or a visual display on a screen. This makes you aware of unconscious processes in your body, such as heart rate, muscle tension or breathing rhythm. Becoming aware of these unconscious physiological processes is the first step towards controlling them.
The biofeedback software or app then evaluates the changes in the measured values and provides a clear training direction. This means that a change in the measured values in the desired direction is achieved through operant conditioning alone, which triggers a relaxation response.
Heart rate monitors and skin conductance meters, respiration meters, skin temperature meters and EMG devices are particularly suitable for these purposes. With these products, you can track your biofeedback values in real time and experience the effects of your mental and physical activities on your physiological states. Through this conscious experience and the resulting control, biofeedback training participants can learn to regulate their physiological states and thus improve their health and performance.
Step 4: Apply relaxation techniques
Based on the findings from stress monitoring, various relaxation techniques can be derived, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation or meditation. Deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation have a physiological effect on stress management by activating the parasympathetic nervous system, which leads to a reduction in stress hormones such as cortisol. This lowers the heart rate, reduces muscle tension and improves blood circulation.
This biofeedback is used to specifically control thoughts, behaviors and feelings and thus effectively reduce stress on the body. Through operant conditioning, behavior is reinforced when combined with relaxation techniques, and thus stress-reducing behaviors can be learned and reinforced. The effect is that by regularly practicing and applying these techniques, you can gain better control over your own stress levels and thus improve your mental and physical health.
Step 5: Real-time biofeedback and adjustments
Real-time biofeedback can be used to optimize and further improve the already known relaxation exercises. By providing feedback on physiological states during exercise, using devices such as heart rate monitors, respiratory monitors, skin temperature meters, EMG devices and skin conductance meters, you can identify which exercises are particularly effective and which are not. Over time, you learn to consciously influence your physiological processes, and the acoustic and visual biofeedback of the devices makes this very easy to implement.
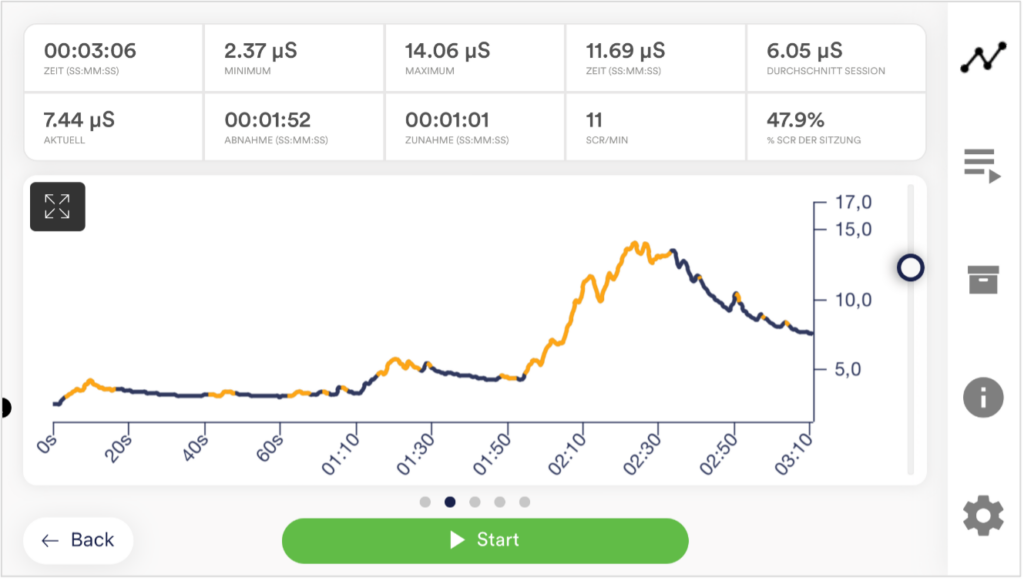
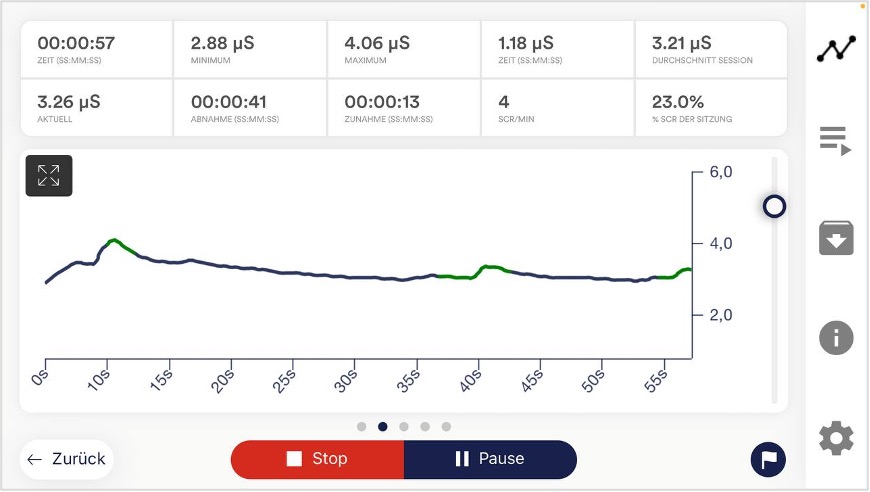
Monitoring the skin conductance level is particularly interesting as it can depict the stress level. The interpretation of the measurement curve requires consideration of tonic and phasic parameters.
The tonic component reflects the long-term conductance level, which is the basic level at which the curve moves. Individual values can vary considerably, with frequent values in the range of 1 to 15 µS.
The phasic components, on the other hand, represent rapid fluctuations, also known as fluctuations or “SCR” (Skin Conductance Responses), of the measured value. These phases are characterized by rapid rises and falls in the curve and can occur spontaneously or in response to a stimulus. A stimulus can be of internal origin (such as thoughts, memories or emotions) or of external origin (such as visual stimuli, acoustic signals or events).
In the context of physiological self-regulation training, the analysis of these curves enables the user to recognize the effectiveness of various exercises, especially in the area of breathing exercises. Here, acoustic and visual biofeedback, based on data from heart rate monitors, EMG devices, skin temperature meters and skin conductance meters, is used to precisely track the physiological state during training. Over time, these measurements enable the user to consciously influence their physiological processes and thus achieve improved self-regulation.
Step 6: Regular biofeedback training
The key to the successful use of biofeedback lies in systematic and regular training. To effectively reduce stress levels, it is advisable to carry out the training at least three to four times a week. This frequency is crucial, as otherwise the body could unlearn the ability to suppress stress signals. The consistent implementation of the training can lead to positive reinforcement, which can contribute to faster and more effective results.
The regular practice of biofeedback training has an effect not only on a physiological but also on a psychological level. It strengthens the psychological aspect of motivation, promotes the release of endorphins and thus contributes to additional stress relief. By continuously integrating biofeedback training into everyday life, a lasting improvement in stress levels can be achieved.
It is important to emphasize that consistent implementation of the training will achieve the best results. This systematic approach makes it possible to make the most of the benefits of biofeedback and experience a lasting improvement in body and mind.
Step 7: Recording and analysis
Biofeedback training generates regular recordings to monitor training progress and identify potential weaknesses in the exercises. By continuously analyzing the recordings, patterns and changes in the physiological processes of the training participant can be identified. The biofeedback software or app helps with the interpretation of the measurement data.
This process is crucial for the self-regulation of stress levels in everyday life, as it enables the participant to understand and influence their physiological reactions without having to apply the feedback directly. The recordings serve as objective data to help the participant become aware of how stress affects the body and how they can respond by taking specific actions.
Through the scientific analysis of biofeedback data, the training participant can recognize that they can effectively control and regulate their physiological processes. This understanding is crucial to minimizing stress reactions and improving overall physical and mental health. The systematic recording and analysis of biofeedback data thus supports the individual optimization of stress management and contributes to the improvement of well-being.
Step 8: Integration of biofeedback into everyday life
It is important to integrate the various relaxation techniques and stress management strategies learned through biofeedback into everyday life. Only the most effective methods should be used based on the precise measurements. With regular training, these new behaviors and techniques can become part of a long-term adaptation, leading to an improved ability to cope with stress and overall relaxation.
One example of integrating these techniques into everyday life could be to consciously take breaks to breathe deeply and relax when you feel stressed or are faced with a challenging task. These breathing pauses could be trained and optimized with the help of biofeedback in order to achieve maximum relaxation and stress reduction. In addition, specific stress management strategies such as positive self-talk or visualization techniques could be used at work or at home to reinforce the effects of biofeedback training and benefit in the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which biofeedback device is best for stress training at home?
The eSense Skin Response is ideal for starting stress training since skin conductance responds particularly quickly and noticeably to stress. It connects via Bluetooth to your smartphone, and the free app guides you through exercises.
How much time do you need daily for biofeedback training?
As little as 10 to 15 minutes of daily training can be sufficient to learn relaxation techniques. The eSense app offers guided exercises with a timer that easily fit into your daily routine.
Can biofeedback measure stress?
Biofeedback does not measure stress directly but rather physiological stress responses such as increased skin conductance, lower skin temperature, or reduced HRV. These values correlate with subjective stress perception.

