Heart rate variability (HRV) is the natural variation in the time intervals between consecutive heartbeats — a key marker of how well your autonomic nervous system adapts to stress, exercise, and recovery. This guide explains how to measure your heart rate variability, what the numbers mean, and how biofeedback training can help you improve it.
What Is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
Heart rate variability (HRV) measures the tiny fluctuations in timing between one heartbeat and the next. Rather than beating like a metronome, a healthy heart constantly adjusts its rhythm in response to breathing, movement, emotions, and dozens of other signals. These beat-to-beat changes reflect how effectively your autonomic nervous system balances the accelerating sympathetic branch with the calming parasympathetic branch. A higher HRV generally signals greater physiological flexibility, while a consistently low HRV may point to elevated stress or reduced resilience. Tracking HRV over time can offer meaningful insights into cardiovascular fitness and nervous system health.
| Measurement Method | Description |
|---|---|
| ECG / EKG | Gold-standard electrode-based recording of cardiac electrical activity |
| Wearables | Smartwatches and fitness bands with optical or ECG-grade sensors |
| Chest Straps | Dedicated heart rate monitors worn around the chest for high-accuracy data |
Key Takeaways
- Heart rate variability (HRV) reflects how well your heart adapts to changing demands — from stress to rest and everything in between.
- A higher HRV is generally associated with better cardiovascular fitness and greater resilience.
- You can measure HRV with ECGs, wearable devices, or dedicated chest-strap monitors.
- HRV is shaped by factors like stress, physical activity, sleep quality, and nutrition.
- Analyzing HRV data provides practical insights into cardiac health and autonomic nervous system balance.
- Regular exercise and effective stress management are among the most reliable ways to support healthy HRV.
- A high HRV is linked to better physical and mental well-being in research studies.
- Day-to-day HRV tracking can guide smarter decisions about training intensity, recovery, and stress management.
Defining Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability (HRV) describes the beat-to-beat changes in the timing between heartbeats. Most people assume the heart beats at a steady pace, but in reality it speeds up and slows down continuously. That constant fine-tuning is a sign of a healthy, flexible autonomic nervous system. When HRV is high, the body can shift quickly between alert, active states and calm, restorative ones — a capacity that matters for both physical performance and emotional balance. HRV is recorded with sensors that capture the precise interval between each R-peak in the cardiac cycle, producing a time series that can be analyzed in several ways.
How Is Heart Rate Variability Measured?
Heart rate variability measurement starts with capturing RR intervals — the exact time gaps between successive heartbeats. Clinical-grade electrocardiograms (ECGs) remain the gold standard, but modern chest-strap monitors and some wrist-worn devices now deliver comparable accuracy. For reliable results, most protocols call for a quiet environment and a recording window of at least two to five minutes, though 24-hour recordings are common in research. The raw data feeds into software that calculates time-domain metrics (like RMSSD), frequency-domain metrics, and nonlinear indices, each revealing a different facet of autonomic regulation.
How Does HRV Analysis Work?
Analyzing heart rate variability turns raw heartbeat data into actionable information about your cardiovascular and nervous system health. Researchers and clinicians rely on several complementary approaches — time-domain analysis, frequency-domain analysis, and nonlinear methods — each offering a different lens on the same data. Time-domain metrics like SDNN and RMSSD summarize overall variability and vagal tone, while frequency-domain analysis separates the signal into low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) bands linked to sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. Together, these metrics help assess stress load, recovery status, and long-term cardiovascular risk.
Techniques for Analyzing Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability data can be examined with several proven techniques, each suited to different goals. Time-domain analysis calculates statistical measures of the intervals between heartbeats — RMSSD, for example, captures short-term vagal activity and is widely used in wearable apps. Frequency-domain analysis breaks the HRV signal into spectral bands, separating sympathetic and parasympathetic contributions. Modern wearables and dedicated software platforms present these results through intuitive dashboards with trend graphs, session comparisons, and color-coded alerts. Understanding which metric matters for your goal — whether it is stress monitoring, athletic recovery, or clinical assessment — is the first step toward putting HRV data to practical use.
- Time-domain analysis (RMSSD, SDNN, pNN50)
- Frequency-domain analysis (LF, HF, LF/HF ratio)
- Nonlinear methods (Poincaré plots, entropy)
- Wearable-integrated dashboards and trend tracking
With sensors like the eSense Pulse, you can measure heart rate variability at home with clinical-grade accuracy. The free eSense app provides real-time feedback and session summaries that are more than sufficient for personal training. If you need deeper statistical analysis — for research or professional practice — the Kubios HRV software is available directly in our shop.
What HRV Data Actually Tells You
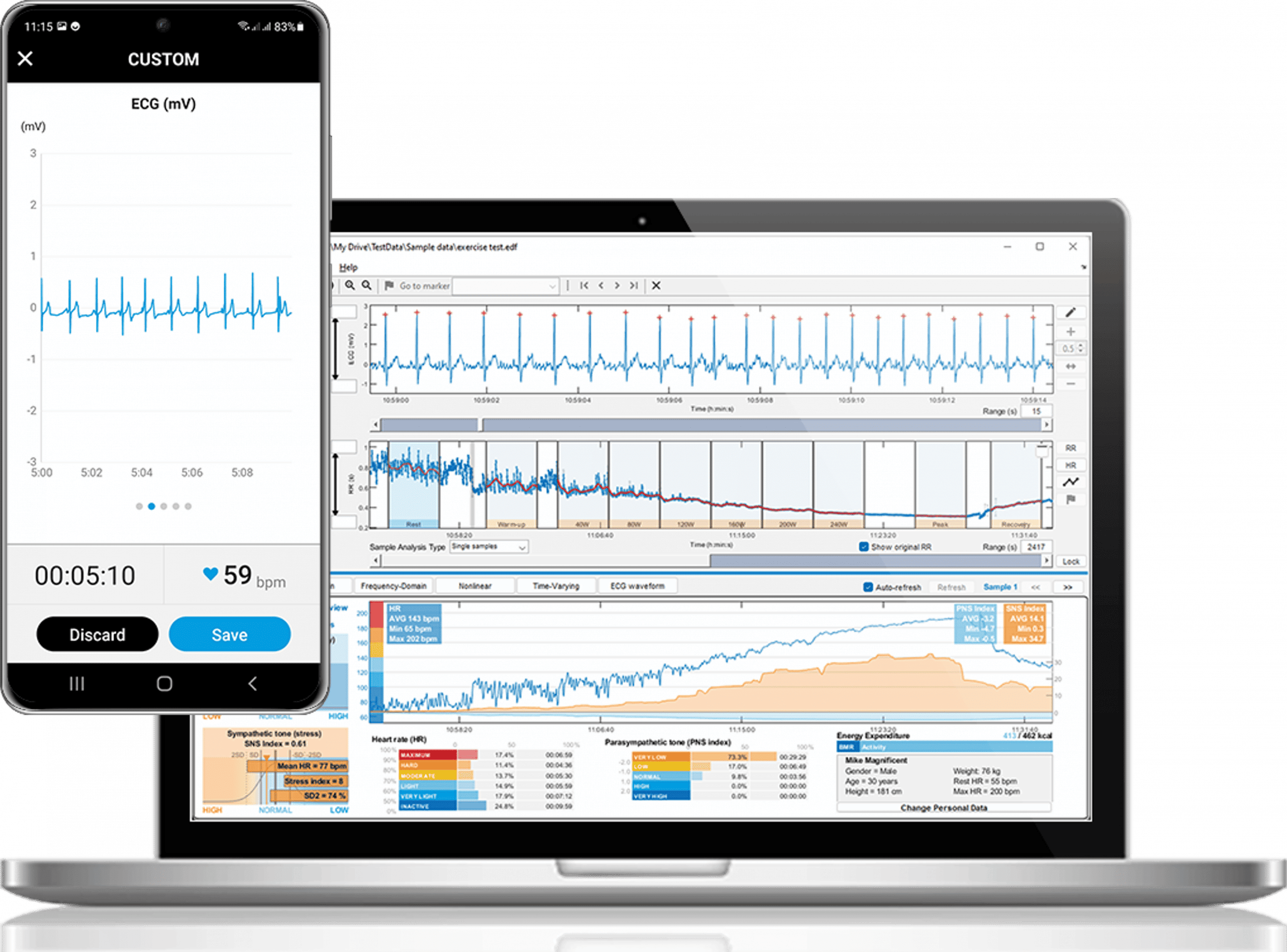
HRV data offers a window into the balance between your sympathetic (“fight or flight”) and parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) nervous systems. A detailed readout can reveal how well you recover from workouts, how deeply stress is affecting your body, and whether your lifestyle changes are making a measurable difference. By tracking trends over weeks and months, you can spot early warning signs of overtraining, burnout, or health issues before they become obvious. That is what makes HRV more than just a number — it is a practical feedback tool for guiding everyday decisions about rest, training, and self-care.
- Autonomic nervous system balance
- Sympathetic vs. parasympathetic tone
- Stress load and recovery capacity
- Training readiness and overtraining risk
- Long-term health and resilience trends
What Factors Influence Heart Rate Variability?
Heart rate variability responds to a wide range of physiological and lifestyle factors. Chronic stress is one of the strongest suppressors — ongoing tension keeps the sympathetic branch dominant and drives HRV down. Conversely, regular relaxation practices can shift the balance toward parasympathetic activity and raise HRV over time. Exercise has a powerful influence as well: moderate, consistent training tends to increase resting HRV, while excessive training without adequate recovery can decrease it. Sleep quality, nutrition, hydration, and even alcohol intake also play measurable roles. Building sustainable habits in each of these areas is the most effective way to support a healthy HRV.
“Chronic stress can significantly lower heart rate variability. At the same time, regular physical activity supports higher HRV — as long as training and recovery stay in balance.”
How Stress and Relaxation Affect HRV
Heart rate variability is one of the most sensitive real-time indicators of how stress and relaxation play out in the body. Under sustained pressure — tight deadlines, emotional strain, sleep deprivation — the sympathetic nervous system stays elevated and HRV drops. When you shift into a relaxed state through deep breathing, meditation, or simply stepping away from a stressful environment, the parasympathetic branch activates and HRV rises. A consistently high resting HRV suggests the body can adapt quickly to stressors and bounce back efficiently, while a persistently low reading may signal that stress is outpacing recovery. That is why building deliberate relaxation into your daily routine — even brief sessions — can make a measurable difference over time.
How Physical Activity Shapes HRV
Heart rate variability and physical activity are closely linked. People who exercise regularly tend to show higher resting HRV, reflecting a heart that adapts efficiently to changing demands. During intense effort, HRV naturally drops as the sympathetic system takes over. In the hours and days after a workout, HRV rebounds — and that recovery pattern is itself a useful signal. If your post-exercise HRV stays depressed longer than usual, it may be a sign to dial back intensity or prioritize sleep. Striking the right balance between training load and recovery is essential for long-term gains in both HRV and overall fitness.
Benefits of a High Heart Rate Variability
A high heart rate variability is widely regarded as a positive marker of cardiovascular health, stress resilience, and overall physiological fitness. Research suggests that individuals with higher HRV tend to recover faster from physical exertion, handle emotional challenges more effectively, and may face a lower risk of cardiovascular events over time. A robust HRV indicates that the autonomic nervous system can switch smoothly between activation and rest, keeping the body responsive without staying in a constant state of alert. While HRV alone does not diagnose any condition, it provides a useful data point for anyone interested in optimizing recovery, performance, and well-being through evidence-based lifestyle choices.
The Link Between HRV and Health
A growing body of research connects higher heart rate variability with favorable health outcomes. Studies have found that people with elevated HRV tend to have lower rates of cardiovascular disease, reduced markers of chronic inflammation, and greater stress tolerance. Higher HRV is also associated with faster post-exercise recovery and better aerobic fitness. These findings make sense physiologically: a flexible autonomic nervous system can allocate resources efficiently, ramping up when action is needed and winding down when it is time to rest. That is why HRV has become a widely used metric for monitoring physical and mental well-being in both clinical and consumer settings.
Practical Tips to Improve Your HRV
Improving heart rate variability comes down to building habits that support autonomic balance. Regular aerobic exercise — running, cycling, swimming — is one of the most effective interventions. Pair it with consistent relaxation practices such as meditation, yoga, or guided breathing exercises. Sleep deserves special attention: both duration and quality directly affect overnight HRV recovery. A balanced diet, adequate hydration, and limiting alcohol and nicotine round out the lifestyle foundations. Finally, HRV biofeedback training — using real-time data to learn conscious control of breathing patterns — is an evidence-based approach that may accelerate improvements. Small, consistent changes tend to produce more lasting results than dramatic short-term interventions.
Using Heart Rate Variability in Daily Life
Heart rate variability is not just a lab metric — it is a practical tool you can use every day to make better decisions about stress management, exercise, and recovery. Morning HRV readings can tell you whether your body is ready for a hard training session or needs an easier day. Real-time HRV monitoring during breathing exercises provides instant feedback on how effectively you are activating your parasympathetic system. Athletes, coaches, and everyday users alike rely on HRV trends to fine-tune the balance between pushing hard and recovering well. Modern wearables and smartphone apps make this kind of data accessible without any clinical setup.
| Use Case | How HRV Helps |
|---|---|
| Stress management | Spot elevated stress early and trigger targeted relaxation |
| Sports and fitness | Optimize training loads and plan recovery days |
| General well-being | Track the balance between daily demands and restoration |
HRV for Stress Management
Heart rate variability gives you an objective read on how your body handles stress — going beyond how you feel to show what is actually happening at a nervous-system level. When HRV drops below your personal baseline, it is a signal that stress is accumulating and recovery has not caught up. Armed with that information, you can respond proactively: a five-minute breathing exercise, a brief walk, or simply pausing to reset. Techniques like coherence breathing (slow, rhythmic inhalation and exhalation at roughly six breaths per minute) have been shown in research to shift autonomic balance toward the parasympathetic side. Over weeks of consistent practice, many people see their baseline HRV trend upward — a sign of growing resilience.
HRV in Sports and Fitness
Heart rate variability has become a go-to metric in sports and fitness for a simple reason: it takes the guesswork out of recovery. By checking HRV each morning, athletes and coaches can decide whether to push for a high-intensity session or dial back to an active recovery day. A high resting HRV generally signals readiness for demanding work, while a dip below baseline suggests the body is still processing the previous session. Over time, consistent HRV monitoring can help prevent overtraining, reduce injury risk, and support steady performance gains. When paired with subjective measures like perceived exertion and sleep quality, HRV data becomes a powerful component of any evidence-based training plan.
FAQ
What is heart rate variability (HRV)?
Heart rate variability (HRV) is the natural variation in time between consecutive heartbeats. It reflects how well your autonomic nervous system adapts to changing physical and emotional demands.
How can I measure my heart rate variability?
You can measure HRV with an ECG-based sensor, a dedicated chest-strap monitor, or a wearable device like a smartwatch. ECG-grade sensors offer the highest accuracy for detailed analysis.
What does a high HRV value mean?
A high HRV generally indicates a healthy, adaptable cardiovascular system and a well-balanced autonomic nervous system. It suggests your body recovers efficiently from stress and physical exertion.
What factors influence HRV?
HRV is shaped by stress levels, physical activity, sleep quality, nutrition, hydration, and lifestyle habits like alcohol and nicotine use.
What techniques are used to analyze HRV?
Common analysis techniques include time-domain methods (RMSSD, SDNN), frequency-domain methods (LF/HF ratio), and nonlinear approaches like Poincaré plots. Each reveals different aspects of autonomic function.
How can I use HRV in daily life?
You can use morning HRV readings to guide training decisions, monitor stress levels throughout the day, and track how lifestyle changes affect your overall recovery and resilience.
How does physical activity affect HRV?
Regular moderate exercise tends to raise resting HRV over time, while overtraining without adequate recovery can lower it. The post-exercise HRV rebound is itself a useful recovery indicator.
Why is analyzing HRV data important?
HRV analysis provides objective insights into cardiovascular health, stress load, and recovery status — information that can guide training, lifestyle adjustments, and early detection of overtraining.
What are the health benefits of a high HRV?
Research links higher HRV with better cardiovascular health, greater stress resilience, lower inflammation markers, and faster recovery from physical and mental challenges.
What are effective ways to improve HRV?
Regular aerobic exercise, consistent relaxation practices (meditation, breathing exercises), quality sleep, balanced nutrition, and HRV biofeedback training are all evidence-based approaches that may help improve HRV.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good heart rate variability?
There is no single “good” number — healthy HRV depends on your age, fitness level, and individual physiology. As a rough guide, RMSSD values in healthy adults typically fall between 20 and 80 ms. What matters most is your personal trend over time: consistent tracking reveals whether your HRV is moving in the right direction.
How can I measure my HRV at home?
An ECG-based chest sensor like the eSense Pulse captures R-R intervals with high precision, making it ideal for detailed HRV analysis. Optical sensors in smartwatches provide a reasonable estimate for daily tracking, though they are less accurate than ECG-grade hardware for clinical or research purposes.
Can HRV be improved with biofeedback training?
Research indicates that regular HRV biofeedback training, breathing exercises, and consistent physical activity can positively influence heart rate variability. Coherence training — slow, rhythmic breathing at approximately six breaths per minute — is one of the most studied protocols and has shown promising results across multiple trials.
Recommended Products for Your Training
- eSense Pulse – Mobile ECG sensor for HRV biofeedback
- FAROS 180 – Professional 1-channel Holter ECG recorder for clinical HRV analysis
- Kubios HRV Scientific – Professional HRV analysis software (SDNN, RMSSD, LF, HF and more)
- Kubios Team Readiness – Team-based HRV monitoring for sports and corporate wellness